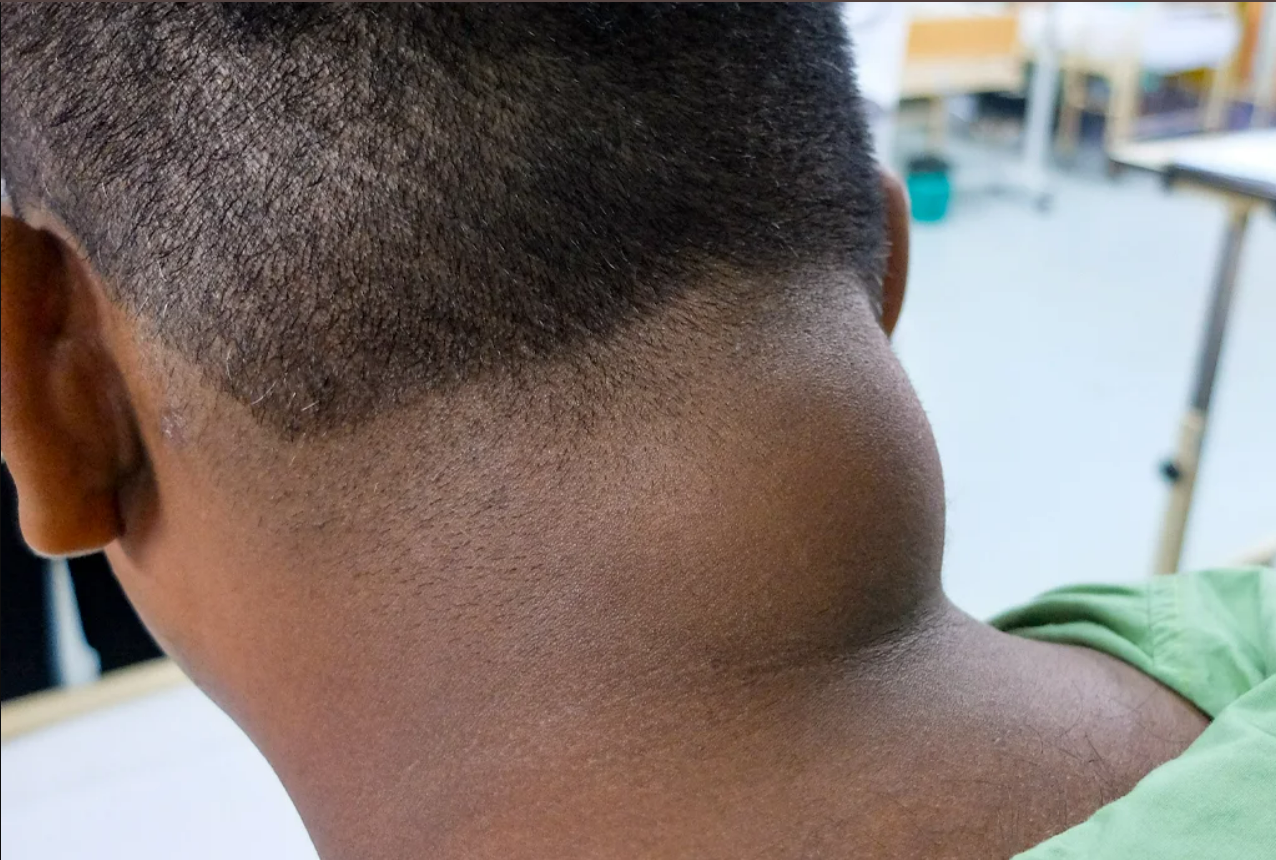
Lipoma
- soft to the touch and moves easily if prodded with your finger
- small, just under the skin, and pale or colorless
- commonly located in the neck, back, or shoulders
- only painful if it presses on a nerve
Lipomas are collections of fatty tissue under the skin and are often painless. They usually form on the neck, back, or shoulders. They’re typically harmless, but you can remove them for cosmetic reasons or if they cause pain.
Learn more about lipoma removal surgery.
Nodule

- small to medium growth that may be filled with tissue, fluid, or both
- usually wider than a pimple and may look like a firm, smooth elevation under the skin
- usually harmless but may cause discomfort if it presses on other structures
- may also be located deep inside the body where you can’t see or feel them
Nodules result from abnormal tissue growth. They appear in common areas like the armpits, groin, and head and neck region.
Seborrheic keratosis

- round, oval, dark-colored growth with a “stuck-on” appearance
- can be located anywhere on the body except for the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
- raised and bumpy with a waxy feel
- may be skin-colored, brown, or black
Seborrheic keratoses (plural of keratosis) are common, harmless skin growths usually seen in older adults. They appear as round, rough spots on the surface of the skin. They can affect many areas of the body, including the chest, shoulders, and back.
Learn how to tell the difference between seborrheic keratosis and melanoma.
Skin tags

- skin growths that can become up to a half-inch long
- same color as your skin or slightly darker
- most likely friction-related cause
- commonly found near the neck, armpits, breasts, groin, stomach, or eyelids
Skin tags are small, fleshy flaps of skin. They usually grow on the neck or in the armpits. They may be the same color as the skin or slightly darker.
Review the differences between moles and skin tags.
Strawberry nevus

- red or purplish raised mark, commonly located on the face, scalp, back, or chest
- appears at birth or in very young children
- gradually gets smaller or disappears as the child ages
Strawberry nevus is a red birthmark also known as a hemangioma. They are most common in young children and usually disappear by age 10 years.
Certain bacterial and viral infections cause skin bumps. Some may go away on their own and may not require treatment. But some will only get worse if they go undiagnosed and untreated.
Boils

- bacterial or fungal infection of a hair follicle or oil gland
- can appear anywhere on the body but are most common on the face, neck, armpit, and buttock
- red, painful, raised bump with a yellow or white center
- may rupture and weep fluid
Boils (aka furuncles) are infected hair follicles that look like red, raised bumps on the skin. They can be painful but eventually go away once they burst and release fluid.
Learn whether you should pop a boil on your own.
Chickenpox

- clusters of itchy, red, fluid-filled blisters in various stages of healing all over the body
- accompanied by fever, body aches, sore throat, and loss of appetite
- remains contagious until all blisters have crusted over
Chickenpox is a common childhood virus characterized by red, itchy bumps that form all over the body. Adults can get it too, and symptoms are often more severe.
Learn about the varicella vaccine to help protect yourself against chickenpox.
Cold sore

- red, painful, fluid-filled blister that appears near the mouth and lips
- affected area will often tingle or burn before the sore is visible
- may be accompanied by mild, flu-like symptoms, such as low fever, body aches, and swollen lymph nodes
Cold sores result from activation of the herpes simplex virus. They appear as red, fluid-filled blisters around your mouth and other areas of your face. They’re most contagious when they burst open but still contagious when they’ve scabbed over.
Learn more about what can trigger the virus that causes cold sores.
Impetigo

- common in babies and children
- irritating rash and fluid-filled blisters that pop easily and form a honey-colored crust
- rash is often located in the area around the mouth, chin, and nose
Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection common in young children. Adults with impetigo often contract the infection from skin-to-skin contact as part of contact sportsTrusted Source.