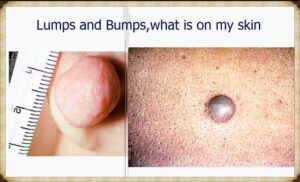
Raised skin bumps are a common dermatological concern and can have various underlying causes, including infections, allergies, and chronic skin conditions. These bumps can appear on any part of the body, and their size, color, and associated symptoms vary widely. Below is a detailed overview of the types of raised skin bumps, causes, and treatment options.
Types of Raised Skin Bumps
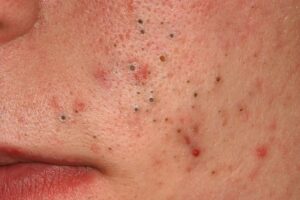
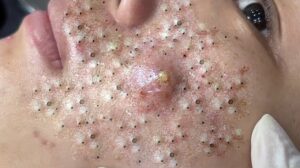
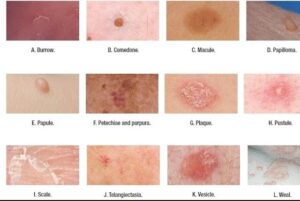
1. Papules
– Small, raised bumps less than 1 centimeter in diameter. They can be red, pink, or flesh-colored and are common in acne.
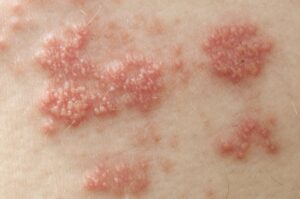
2. Nodules
– Larger than papules, nodules are firm and extend deeper into the skin. These bumps can be painful and may require medical treatment, often appearing in cystic acne or severe skin infections.
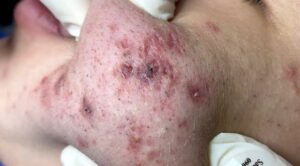
3. Pustules
– Small, pus-filled lesions that often accompany infections, particularly acne or folliculitis. These bumps appear red at the base with a white or yellow center due to pus accumulation.

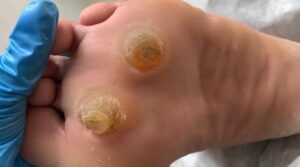
4. Cysts
– Closed, sac-like bumps filled with fluid or semi-solid material. They form deeper in the skin than pustules and can grow larger if untreated, often found in cases of severe acne or sebaceous cysts.
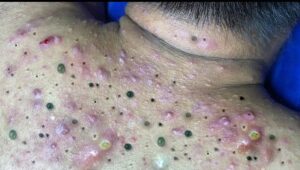
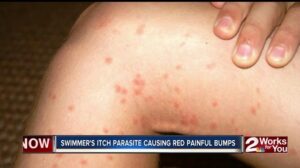
5. Hives (Urticaria)
– Raised, red, or pale welts on the skin, typically itchy, and often caused by allergic reactions. Hives can be temporary or chronic.
6. Blisters (Vesicles or Bullae)
– Fluid-filled bumps caused by friction, burns, or infections. Vesicles are small, whereas bullae are larger.
Common Causes of Raised Skin Bumps
1. Acne
– One of the most common causes, acne causes a mix of papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts due to the clogging of hair follicles with oil and dead skin cells. This results in inflammation and raised bumps.
2. Allergic Reactions
– Allergic reactions, such as to food, medications, or environmental factors, often lead to hives. These reactions cause the body to release histamine, resulting in itching and raised welts.
3. Infections
– Various bacterial, viral, and fungal infections can cause raised skin bumps. For instance:
– Impetigo
– A bacterial infection that creates red sores or blisters, primarily in children.
– Molluscum Contagiosum
– A viral infection causing smooth, flesh-colored bumps that spread through skin contact.
– Herpes Simplex
– Leads to fluid-filled blisters around the mouth or genital area.
4. Insect Bites and Stings
– Bites from mosquitoes, spiders, and other insects can cause itchy, raised bumps. Some stings may also trigger an allergic reaction, making the bumps more severe.
5. Chronic Skin Conditions
– Skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and rosacea are also characterized by raised bumps. Eczema, for example, causes patches of inflamed, itchy skin, while psoriasis results in red, scaly plaques.
Diagnosis of Skin Bumps
For accurate diagnosis, a healthcare professional will usually take a detailed history and conduct a physical examination. In some cases, a biopsy or culture may be necessary. Blood tests are sometimes used to rule out infections or autoimmune conditions. Dermatologists often use a dermatoscope—a specialized magnifying tool—to examine the skin more closely.
Treatment Options

1. Topical Treatments
– Mild cases of acne or infections may be treated with over-the-counter topical treatments containing benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or hydrocortisone.
2. Antibiotics
– For bacterial infections like impetigo, doctors may prescribe topical or oral antibiotics.
3. Antihistamines
– These are commonly used to manage allergic reactions that lead to hives, reducing the itch and inflammation.
4. Steroid Injections
– Cystic acne and inflamed nodules may benefit from corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and speed up healing.
5. Surgical Removal
– For larger cysts, minor surgical removal might be necessary. This is often a quick outpatient procedure where the cyst is drained or excised.
Prevention and Home Care
Proper skincare, such as keeping the skin clean and avoiding known allergens, can prevent some types of bumps. Regularly washing with gentle cleansers can reduce acne breakouts, while using sunscreen may prevent sun-induced skin conditions. Keeping insect repellents on hand and avoiding scented lotions can also help prevent bites and hives.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many raised skin bumps are harmless, some may indicate a more serious condition. Seek medical attention if a bump is:
– Persistent and does not improve with home care
– Accompanied by symptoms like fever or fatigue
– Painful, large, or rapidly changing in appearance
– Associated with other symptoms, like difficulty breathing or swelling, which could indicate an allergic reaction