Blackhead Treatment
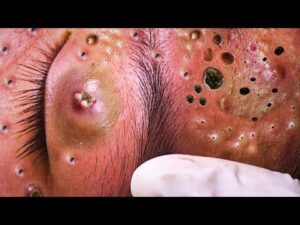
This blockage can lead to a range of lesions, including whiteheads, blackheads, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts, with severity varying depending on the individual and their skin type.
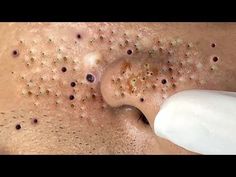
One of the primary causes of pimples is hormonal changes, especially during puberty.
Hormones, particularly androgens, increase the production of sebum from sebaceous glands.
This excess oil can combine with dead skin cells to create a clog in the follicle.
If bacteria, such as *Propionibacterium acnes* (or *Cutibacterium acnes*), are present in the follicle, it can multiply and cause inflammation, resulting in redness, swelling, and pus.
The types of pimples can vary in appearance and severity.
Whiteheads are small, raised, white bumps caused by clogged pores that remain closed, while blackheads are open comedones that appear dark due to oxidation. Papules are small red or pink bumps that are inflamed but do not contain pus, while pustules are inflamed lesions with a white or yellow center, indicating the presence of pus.
More severe types, such as nodules and cysts, are large, deep, and painful; they occur when the infection goes deeper into the skin, potentially causing scarring if not treated.
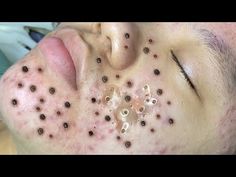
Several factors can contribute to the development of pimples beyond hormones.
Genetics, diet, stress, and skincare habits can influence the occurrence and severity of pimples. Genetics, for example, can determine skin type and predisposition to acne.
Certain foods, especially those with high glycemic indexes (like sugary and processed foods), have been linked to acne, though research is ongoing in this area.
Stress can exacerbate pimples by stimulating hormone release, especially cortisol, which may increase oil production.
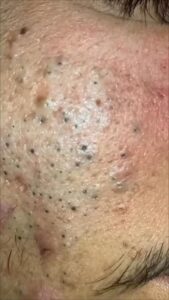
There are numerous treatment options for pimples, ranging from over-the-counter (OTC) topical treatments to prescription medications. OTC products often contain ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and sulfur, which work by reducing oil, unclogging pores, and killing bacteria.
For more severe acne, dermatologists may prescribe topical retinoids, antibiotics, or oral medications like isotretinoin (Accutane).
Hormonal treatments, such as birth control pills or anti-androgen medications, may also be effective for those whose acne is primarily hormonally driven.
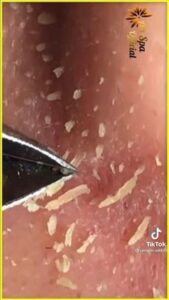
Proper skincare can be essential in managing and preventing pimples.
Using a gentle cleanser to wash the face twice daily, avoiding over-washing, and choosing non-comedogenic products that don’t clog pores are some key steps. Exfoliating once or twice a week can also help remove dead skin cells, but over-exfoliation can irritate the skin and worsen acne.
It is generally advisable to avoid picking or squeezing pimples, as this can introduce bacteria and lead to scarring.
In addition to these treatments, lifestyle changes, like maintaining a balanced diet, reducing stress, and staying hydrated, can positively impact skin health. Although pimples can be challenging and impact self-esteem, many effective treatments are available, and preventive skincare practices can help manage and reduce breakouts over time.